A-Level经济知识点介绍:elasticity分析题思路指津
elasticity算是经济U1的重点之一,很多同学也容易混淆这里的知识点,今天我就以往年的一道真题来给大家讲一下解题思路,希望大家有所启发,能在日后的做题中举一反三。
2014年1月真题

名 师解析
首先看题目,让你判断是elastic还是inelastic,我们要想到这道题考查的是弹性里面price elasticity of supply部分的内容。题目中“discuss”提示词,以及括号里10分的题目分值,可知这里要考查两面性思维,因此要从正反两个角度去答题。
【10分题给分细则:KAA6+Ev4】
✦正面思考:
第 一步:回答PES(price elasticity of supply)定义、elastic与inelastic的区别。
Price elasticity of supply:a measure of the responsiveness of quantity supplied to a change in price. When PES>1, it is elastic; when 0
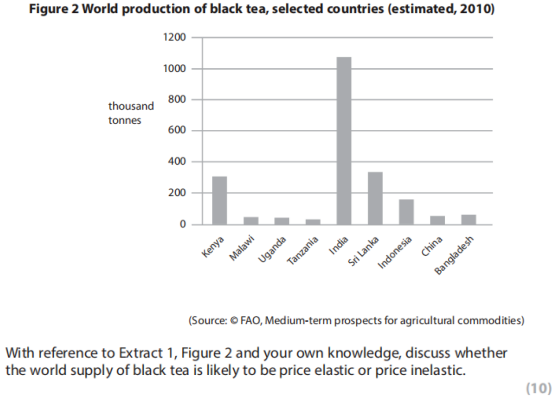
第二步:结合材料去判断black tea的供给价格弹性是elastic还是inelastic。
Price elasticity of supply of black tea is likely to be inelastic.【An1】This is because:
1、The world’s main producer--India and Sri Lanka have no extra land available for tea cultivation and Kenya has very little land for planting tea. The land for tea gardens is very difficult to find. Some land is available in Rwanda and Vietnam but this takes time to develop.【Ap1】
2、Tea bushes can only be harvested six years after they are planted. So the supply can’t keep the pace of the demand. 【Ap1】
3、The stock can reduce price fluctuation. But buffer stock scheme was never attempted because of major obstacle of funding, storability and the difficulty of achieving agreement from tea growers.【Ap1】
✦反面思考:
第三步:逆向思维,black tea的供给有可能会是inelastic的(这里是结合题目中的暗示),或者是uncertain(这里是需要自己结合行业背景进行合理发挥)。
In the long run, Rwanda and Vietnam may develop more land to produce black tea. And technical progress may solve the difficulty of stock or reduce the period of planting. In these case, the PES may become elastic. 【Ev2】
Besides, tea plantation depends on climate. If there is drought or flood, the supply will decrease. And farmers’entry and exit to the tea market also influences PES. So there is no guarantee that PES will be elastic in the long run. 【Ev2】
(做笔记:长短期思考方式所带来的不同结论正是常见的evaluation得分点。)
知识拓展:
为什么stock(库存)可以减少价格波动呢?
stock就像一个供给储备器一样,当市场的价格比较低的时候,生产者会有惜售心理,行动上就会倾向于囤货等待高价再出售,此时market supply减少,推动价格上升;而当价格比较低的时候,生产者就会急于出货赚取更多收入,此时market supply增加,使得价格下降。所以,有stock时的价格波动范围会小于没有stock时的价格波动范围。也正因如此,政府会对很多农作物(如棉花、大豆、玉米等)进行囤积储备,在丰收年份购买过剩的产品,使得价格不要降的太低,维护农民的收入与生产积极性;在欠收年份出售之前储备的产品,使得价格不要太高,保证普罗大众能够买得起这些生活所必需之物。





